Blackthorn
Botanical name: Prunus spinosa
Family: Rose (Rosaceae)
Collectability: plentiful, common, widespread
Main benefit

 regulates and cleanses the digestive system
regulates and cleanses the digestive system
Use - overview









Features and Identification
Habitat
Type: scrub, woods, hedges
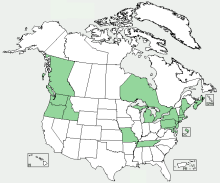
Distribution: throughout northern hemisphere
General
Growth type: tree
Cycle: deciduous
Height: up to 4 meters
Other: tangled branches
 Leaf
Leaf
Shape: pointed oval
Arrangement: alternate
Edge: finely toothed
Other: small
 Trunk
Trunk
Colour: dark brown
Texture: large spines throughout
 Flower
Flower
Diameter: 10 mm
Arrangement: on spines
When: before leaves
Colour:
 Fruit
Fruit
Shape: round
Colour: blue-black
Size: up to 15 mm
Other: called "sloe", bloom on young fruit
Type: scrub, woods, hedges
Distribution: throughout northern hemisphere
General
Growth type: tree
Cycle: deciduous
Height: up to 4 meters
Other: tangled branches
 Leaf
LeafShape: pointed oval
Arrangement: alternate
Edge: finely toothed
Other: small
 Trunk
TrunkColour: dark brown
Texture: large spines throughout
 Flower
FlowerDiameter: 10 mm
Arrangement: on spines
When: before leaves
Colour:

 Fruit
FruitShape: round
Colour: blue-black
Size: up to 15 mm
Other: called "sloe", bloom on young fruit
Distribution Map
Caution Notes
 The leaves, bark, flowers and seeds contain or produce hydrogen cyanide in contact with water. Hydrogen cyanide, also known as Prussic acid, may be safe in very small quantities. May be driven off by heat. Very bitter with smell of almonds. Consume in moderation.
The leaves, bark, flowers and seeds contain or produce hydrogen cyanide in contact with water. Hydrogen cyanide, also known as Prussic acid, may be safe in very small quantities. May be driven off by heat. Very bitter with smell of almonds. Consume in moderation.Spines may cause septic wounds.
When Available?
 from May
from May all year
all year April and May
April and May September and October
September and OctoberParts with black and white icons are for non-culinary use
Culinary Use
Flavour
Rating and Description:

 very astringent and acid; better after frost or when made into jelly, syrup or for flavouring spirits
very astringent and acid; better after frost or when made into jelly, syrup or for flavouring spirits
How to Consume
 raw, jelly, syrup, flavouring spirits
raw, jelly, syrup, flavouring spirits
Special preparation
 for flavouring spirits prick the fruit; see "fruit" on the Parts page for instructions on making syrup.
for flavouring spirits prick the fruit; see "fruit" on the Parts page for instructions on making syrup.
Used as ...
 food, flavouring
food, flavouring
Rating and Description:

 very astringent and acid; better after frost or when made into jelly, syrup or for flavouring spirits
very astringent and acid; better after frost or when made into jelly, syrup or for flavouring spiritsHow to Consume
 raw, jelly, syrup, flavouring spirits
raw, jelly, syrup, flavouring spirits Special preparation
 for flavouring spirits prick the fruit; see "fruit" on the Parts page for instructions on making syrup.
for flavouring spirits prick the fruit; see "fruit" on the Parts page for instructions on making syrup. Used as ...
 food, flavouring
food, flavouringMedicinal Use
Action:

 aperient, astringent, depurative, diaphoretic, diuretic, febrifuge, laxative, stomachic
aperient, astringent, depurative, diaphoretic, diuretic, febrifuge, laxative, stomachic
May treat:
 cystitis, gout, rheumatism
cystitis, gout, rheumatism
 diarrhoea
diarrhoea

 aperient, astringent, depurative, diaphoretic, diuretic, febrifuge, laxative, stomachic
aperient, astringent, depurative, diaphoretic, diuretic, febrifuge, laxative, stomachic May treat:
 cystitis, gout, rheumatism
cystitis, gout, rheumatism diarrhoea
diarrhoea
Other Use
 green dye
green dye (trunk) timber: hard, for turnery, carving etc., bark: tannin, yellow dye (boiled in alkali)
(trunk) timber: hard, for turnery, carving etc., bark: tannin, yellow dye (boiled in alkali) dark grey to green dye; unripe juice: laundry marking (almost indelible)
dark grey to green dye; unripe juice: laundry marking (almost indelible)
Collection, Storing and Notes
Collection
 best picked after first frost
best picked after first frost
 best picked after first frost
best picked after first frost
Key
Plant parts:
 leaf
leaf
 stem or trunk
stem or trunk
 sap
sap
 root, bulb, tuber and other below ground parts
root, bulb, tuber and other below ground parts
 flower
flower
 fruit
fruit
 seed
seed
Parts with black and white icons in the availability section are for non-culinary use
Use:
 culinary use
culinary use
 medicinal use
medicinal use
 household use
household use
Other:
 caution
caution
 leaf
leaf stem or trunk
stem or trunk sap
sap root, bulb, tuber and other below ground parts
root, bulb, tuber and other below ground parts flower
flower fruit
fruit seed
seedParts with black and white icons in the availability section are for non-culinary use
Use:
 culinary use
culinary use medicinal use
medicinal use household use
household useOther:
 caution
caution
Glossary
Glossary of Medicinal Terms and Nutritive Substances
- aperient: mild laxative
- astringent: causes localised contraction of blood vessels and tissue, reducing the flow of blood, mucus, diarrhoea etc.
- depurative: eliminates toxins and purifies the system, especially the blood
- diaphoretic: promotes perspiration, aids the skin in elimination of toxins
- diuretic: increases secretion and elimination of urine
- febrifuge: reduces fever; use only for dangerously high temperature; a raised temperature is the body's way of burning up the pathogen
- laxative: evacuates the bowels or softens stools
- stomachic: treats stomach disorders