Garden Sorrel
Information about properties also applies to Common Sheep Sorrel R. acetosella
Botanical name: Rumex acetosa
Family: Dock (Polygonaceae)
Collectability: plentiful, common, widespread, good, weed
Main benefit
 Blood cleanser, source of Vitamin C
Blood cleanser, source of Vitamin C
Use - overview











Features and Identification
Habitat
Type: grassy places
Distribution: throughout northern hemisphere
Prefers: iron rich soil
General
Growth type: herb
Cycle: perennial
Height: up to 90 cm
Other:
 Leaf
Leaf
Shape:long arrow, upper clasp stem
Texture: smooth
Arrangement: alternate
Edge: smooth
 Flower
Flower
Diameter: tiny
Arrangement: spikes, loosely branched
Colour:
 Seed
Seed
Size: tiny
Type: grassy places
Distribution: throughout northern hemisphere
Prefers: iron rich soil
General
Growth type: herb
Cycle: perennial
Height: up to 90 cm
Other:
 Leaf
LeafShape:long arrow, upper clasp stem
Texture: smooth
Arrangement: alternate
Edge: smooth
 Flower
FlowerDiameter: tiny
Arrangement: spikes, loosely branched
Colour:

 Seed
SeedSize: tiny
Distribution Map
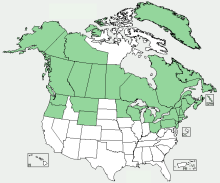
Distribution of Garden Sorrel Rumex acetosa
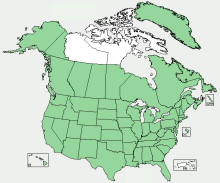
Distribution of Common Sorrel R. acetosella
Caution Notes
 Contains oxalic acid. Oxalic acid can bind up other minerals, especially calcium. May aggravate rheumatic conditions, kidney stones, hyper acidity or osteoporosis. May be reduced by cooking, possibly also if eaten with a source of salts derived from methyl salicylate (salicylic acid etc.) from sources such as dried Meadowsweet. Eat in moderation.
Contains oxalic acid. Oxalic acid can bind up other minerals, especially calcium. May aggravate rheumatic conditions, kidney stones, hyper acidity or osteoporosis. May be reduced by cooking, possibly also if eaten with a source of salts derived from methyl salicylate (salicylic acid etc.) from sources such as dried Meadowsweet. Eat in moderation.
When Available?
 February to August
February to August all year
all year May to August
May to August July to October
July to October
Culinary Use
Flavour
Rating and Description:

 lemony
lemony
How to Consume
 raw, juiced for rennet
raw, juiced for rennet
 cooked, flour
cooked, flour
 cooked
cooked
 raw, flour
raw, flour
Special preparation
 As the seed is small and could easily pass through the digestive system, it is best to grind them to allow absorption of nutrients.
As the seed is small and could easily pass through the digestive system, it is best to grind them to allow absorption of nutrients.
Nutrition
 Vitamin C
Vitamin C
Used as ...
 food, curdling agent, lemon substitute
food, curdling agent, lemon substitute


 food
food
Rating and Description:

 lemony
lemonyHow to Consume
 raw, juiced for rennet
raw, juiced for rennet cooked, flour
cooked, flour cooked
cooked raw, flour
raw, flourSpecial preparation
 As the seed is small and could easily pass through the digestive system, it is best to grind them to allow absorption of nutrients.
As the seed is small and could easily pass through the digestive system, it is best to grind them to allow absorption of nutrients.Nutrition
 Vitamin C
Vitamin CUsed as ...
 food, curdling agent, lemon substitute
food, curdling agent, lemon substitute

 food
food
Medicinal Use
Action:
 anthelmintic, antiscorbutic, astringent, depurative, diuretic, febrifuge, laxative
anthelmintic, antiscorbutic, astringent, depurative, diuretic, febrifuge, laxative
 astringent, diuretic, haemostatic
astringent, diuretic, haemostatic
May treat:
 internal: skin complaints; external: cooked and mushed (poultice): brings boils and abscesses to a head; itchy skin and ringworm (juice mixed with fumitory)
internal: skin complaints; external: cooked and mushed (poultice): brings boils and abscesses to a head; itchy skin and ringworm (juice mixed with fumitory)
 jaundice, gravel, kidney stones
jaundice, gravel, kidney stones
 anthelmintic, antiscorbutic, astringent, depurative, diuretic, febrifuge, laxative
anthelmintic, antiscorbutic, astringent, depurative, diuretic, febrifuge, laxative astringent, diuretic, haemostatic
astringent, diuretic, haemostaticMay treat:
 internal: skin complaints; external: cooked and mushed (poultice): brings boils and abscesses to a head; itchy skin and ringworm (juice mixed with fumitory)
internal: skin complaints; external: cooked and mushed (poultice): brings boils and abscesses to a head; itchy skin and ringworm (juice mixed with fumitory) jaundice, gravel, kidney stones
jaundice, gravel, kidney stones
Other Use
 grey-blue dye, silver polish
grey-blue dye, silver polish dark green to brown dye (no mordant)
dark green to brown dye (no mordant)
Collection, Storing and Notes
Drying
Dry to store
Note
Avoid iron (except s/s) and aluminium implements. Plant will react with iron or leach aluminium into the food due to its high acidity.
Dry to store
Note
Avoid iron (except s/s) and aluminium implements. Plant will react with iron or leach aluminium into the food due to its high acidity.
Key
Plant parts:
 leaf
leaf
 stem or trunk
stem or trunk
 sap
sap
 root, bulb, tuber and other below ground parts
root, bulb, tuber and other below ground parts
 flower
flower
 fruit
fruit
 seed
seed
Use:
 culinary use
culinary use
 medicinal use
medicinal use
 household use
household use
Other:
 caution
caution
 leaf
leaf stem or trunk
stem or trunk sap
sap root, bulb, tuber and other below ground parts
root, bulb, tuber and other below ground parts flower
flower fruit
fruit seed
seedUse:
 culinary use
culinary use medicinal use
medicinal use household use
household useOther:
 caution
caution
Glossary
Glossary of Medicinal Terms and Nutritive Substances
- anthelmintic: expels parasites from the gut (see also Vermifuge)
- antiscorbutic: prevents scurvy, contains Vitamin C
- astringent: causes localised contraction of blood vessels and tissue, reducing the flow of blood, mucus, diarrhoea etc.
- depurative: eliminates toxins and purifies the system, especially the blood
- diuretic: increases secretion and elimination of urine
- febrifuge: reduces fever; use only for dangerously high temperature; a raised temperature is the body's way of burning up the pathogen
- haemostatic: controls bleeding (see astringent)
- laxative: evacuates the bowels or softens stools